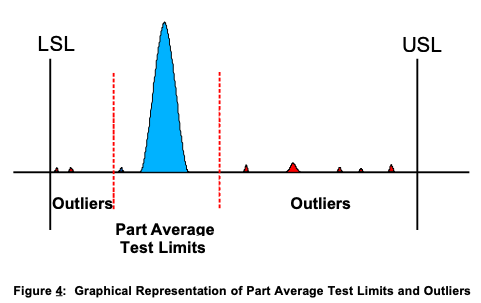
車用電子協會Automotive Electronics Council提供半導體電子元件產業一項品質準則:為了提升車用電子設備的可靠性及品質,勢必要透過一種方法來因應數量龐大的半導體電子元件,而這方法就是Part Average Testing(PAT)零件平均測試。
This guideline presents a statistically based method, called part average testing (PAT), for removing parts with abnormal characteristics (outliers) from the semiconductors supplied per AEC-Q100 and AEC-Q101. The test limits used in PAT are established based on a sample of the electrical test results for that particular part with its unique design and processing. Each part design and its associated processing will show a unique distribution of test results for each test requirement and this data is the basis for establishing PAT limits. The principles described in this guideline are applicable to packaged or unpackaged die. For a further discussion of PAT and its possible use to provide Known Good Die, see Appendix 1.
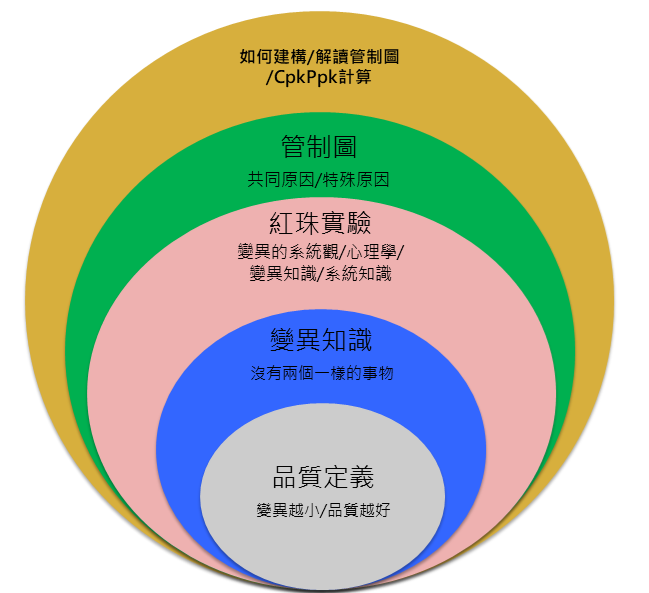
零件平均測試的一大重點,就是針對一般統計位置與離散程度的「平均值」及「標準差」提出了新的概念:「Robust Mean」&「Robust Sigma」。所謂的Robust就是指可靠度更佳、品質更好的電子元件,而實務上達成robust的作法則是透過去除outlier的方式執行。它的概念很簡單:捨棄平均數,改用中位數;捨去樣本前後50%的數據,保留中間50%的數據並估算其標準差。這兩者都能減少平均數被極端值影響的狀況。
這種作法的考量因素在於,平均值極易受到離群值的影響而被「干擾」,進而呈現為與實際分配不符的錯誤指標。採用「Robust Mean」&「Robust Sigma」則可以確保數據不會被離群值干擾,而呈現篩選過的主要分配的樣貌,但這要你的原始分配得是常態分配才成立。
�Static PAT Limits = Robust Mean ± Robust Sigma = Q2 ± [(Q3-Q1)/1.35]
*(Q3-Q1)/1.35是統計上估算標準差的其中一種方法。
PAT的限制顯而易見,首先這項品質特性得先經過SPC控制,再由全檢的方式得到所有電子元件的測試資料並以此計算Robust Mean & Robust Sigma,過程中已然耗費過多成本;但相較於車用市場的後續失效成本來說,或許這也是不得已的作法。
瀏覽次數: -